Atrial fibrillation (AFib), affecting nearly six million Americans, is the most prevalent form of arrhythmia. Characterized by an irregular heartbeat, AFib can lead to significant complications like stroke and heart failure. Effective management often hinges on consistent monitoring, primarily through Electrocardiograms (ECGs).
What is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
AFib occurs when the heart's electrical signals become erratic, causing the heart muscles to contract irregularly. This irregularity disrupts blood flow and increases the risk of clot formation, potentially leading to a stroke if a clot moves to the brain.
Symptoms of AFib
Symptoms vary widely; some individuals experience no symptoms, while others may encounter:
- Palpitations: Feeling a quick, fluttering heartbeat.
- Weakness: General fatigue can accompany AFib.
- Shortness of Breath: Especially noticeable during physical activities.
- Chest Pain: Often causing significant discomfort.
- Dizziness: Experiencing lightheadedness or faint spells.
- Immediate medical consultation is advisable if these symptoms appear, as early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing further complications.
Risk Factors for AFib
Risk increases with age and is compounded by:
- Existing heart conditions: Heart failures or previous heart attacks heighten AFib risks.
- High blood pressure: Common in 60-80% of AFib patients.
- Other conditions: Diabetes, thyroid issues, and chronic lung diseases also elevate risks.
- Lifestyle factors: Obesity, excessive alcohol intake, and high stress are contributors.
- Family history: Genetic predisposition plays a role in approximately 30% of cases.
ECG's Role in Diagnosing AFib
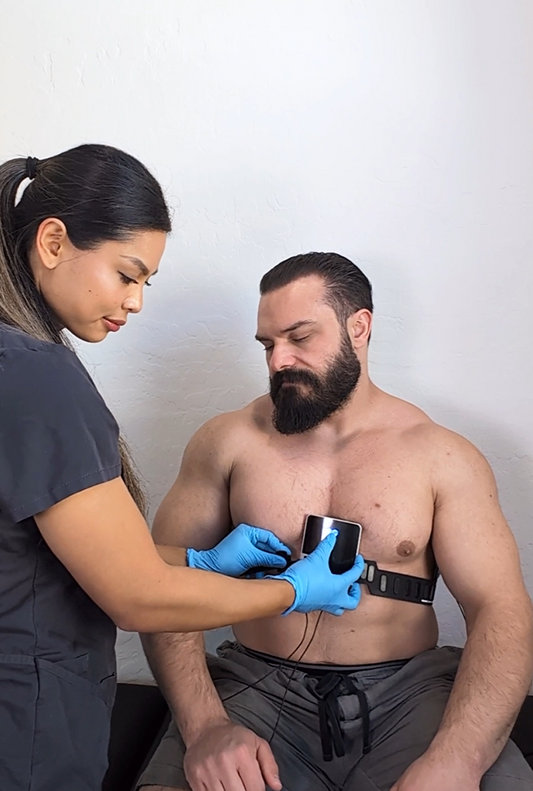
An ECG, a straightforward and non-invasive test, is instrumental in diagnosing AFib. It involves placing electrodes on the body to capture electrical impulses of the heart, which are then displayed as waves. These readings help physicians detect irregularities in the heart’s rhythm. Due to the intermittent nature of AFib, continuous monitoring might be necessary for accurate diagnosis.
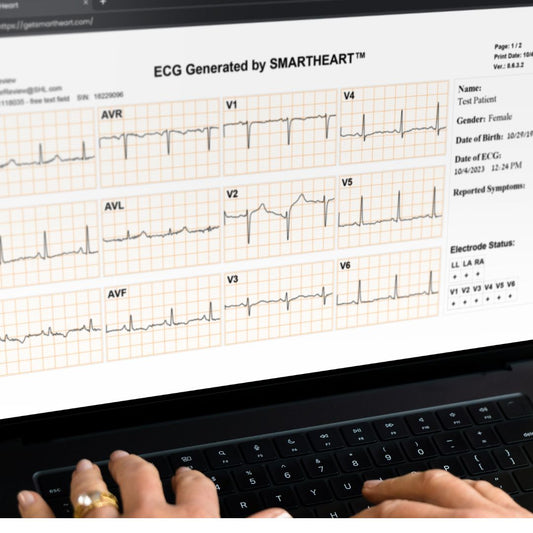
A 12-lead ECG is generally considered more sensitive and accurate for detecting atrial fibrillation (AFib) compared to a 6-lead ECG due to several reasons:
- Comprehensive View of the Heart: A 12-lead ECG provides a more comprehensive view of the heart's electrical activity, capturing information from different angles. This allows for better detection of irregular heart rhythms like AFib.
- More Detailed Information of the Heart’s Electrical Activity: A 12-lead ECG offers more detailed and varied waveform data from different parts of the heart, which is crucial for identifying the erratic electrical activity characteristic of AFib.
In contrast, a 6-lead ECG, while still useful, provides less information and fewer perspectives of the heart's electrical activity. It typically includes fewer leads that monitor the atrial activity, which can limit its sensitivity in detecting AFib.
Overall, while a 6-lead ECG can still be effective, particularly in settings where quick or portable monitoring is needed, a 12-lead ECG is generally preferred for its thoroughness and accuracy in diagnosing atrial fibrillation.
Managing AFib
Management includes lifestyle adjustments, medications, and possibly medical procedures. Recommendations often encompass:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in sodium and fats.
- Regular moderate exercise.
- Avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to alleviate heart strain.
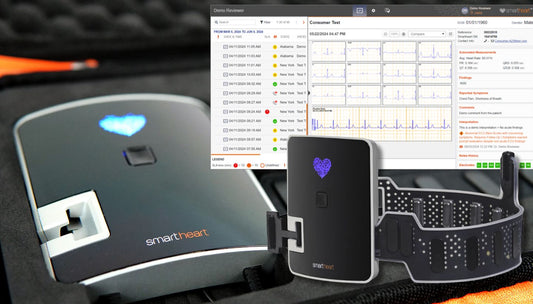
Home Monitoring of AFib
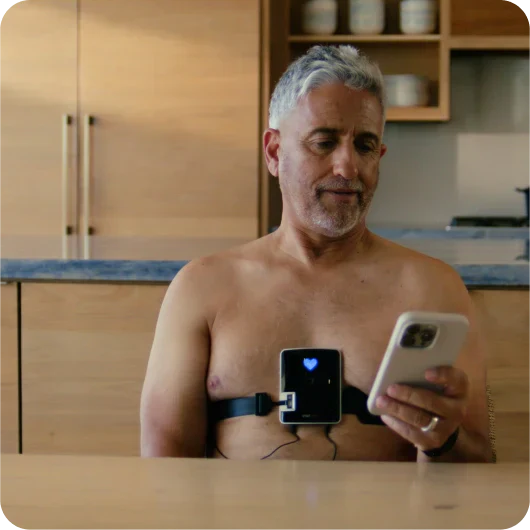
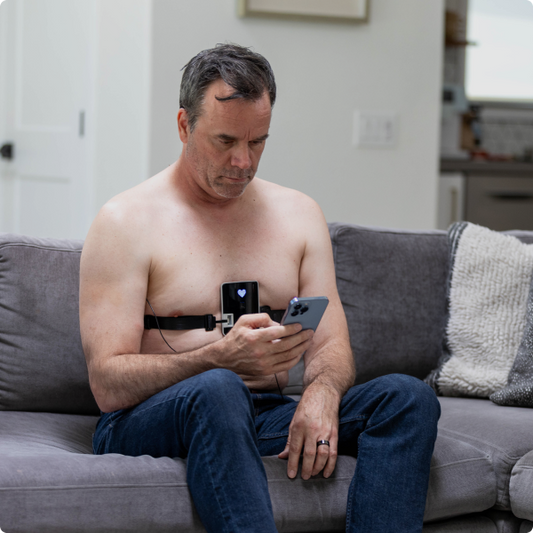
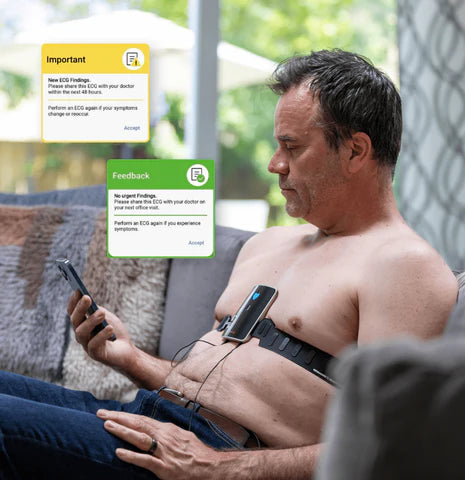
Portable ECG devices have transformed patient involvement in health management, allowing for regular monitoring at home. These devices are especially beneficial for patients at high risk, providing data that help in making informed treatment decisions.
Regular Monitoring and Home ECG Benefits
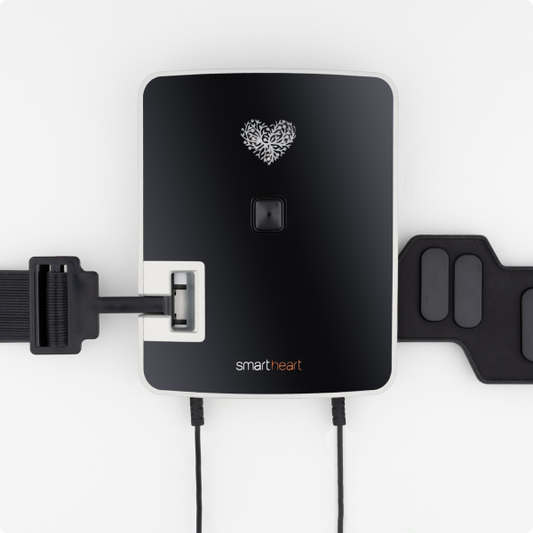
Home monitoring with a 12-lead ECG like SmartHeart not only facilitates early detection of irregular rhythms but also enhances patient autonomy in health management. Benefits include:
- Immediate detection of abnormalities.
- More comprehensive view of the heart.
- Reduced need for frequent clinical visits.
- Easy sharing of data with healthcare providers.
Conclusion
Staying informed about AFib and maintaining regular monitoring are pivotal. a SmartHeart 12-lead ECG, with 24/7 review by board-certified cardiologists, offers an excellent solution for at-home monitoring, combining convenience with reliability, ensuring patients can actively manage their condition with confidence. Consider SmartHeart for a comprehensive approach to AFib management.
This format delivers the key information in a concise manner, aimed at educating consumers about AFib while highlighting the importance and benefits of using an ECG device like SmartHeart for ongoing heart health monitoring.